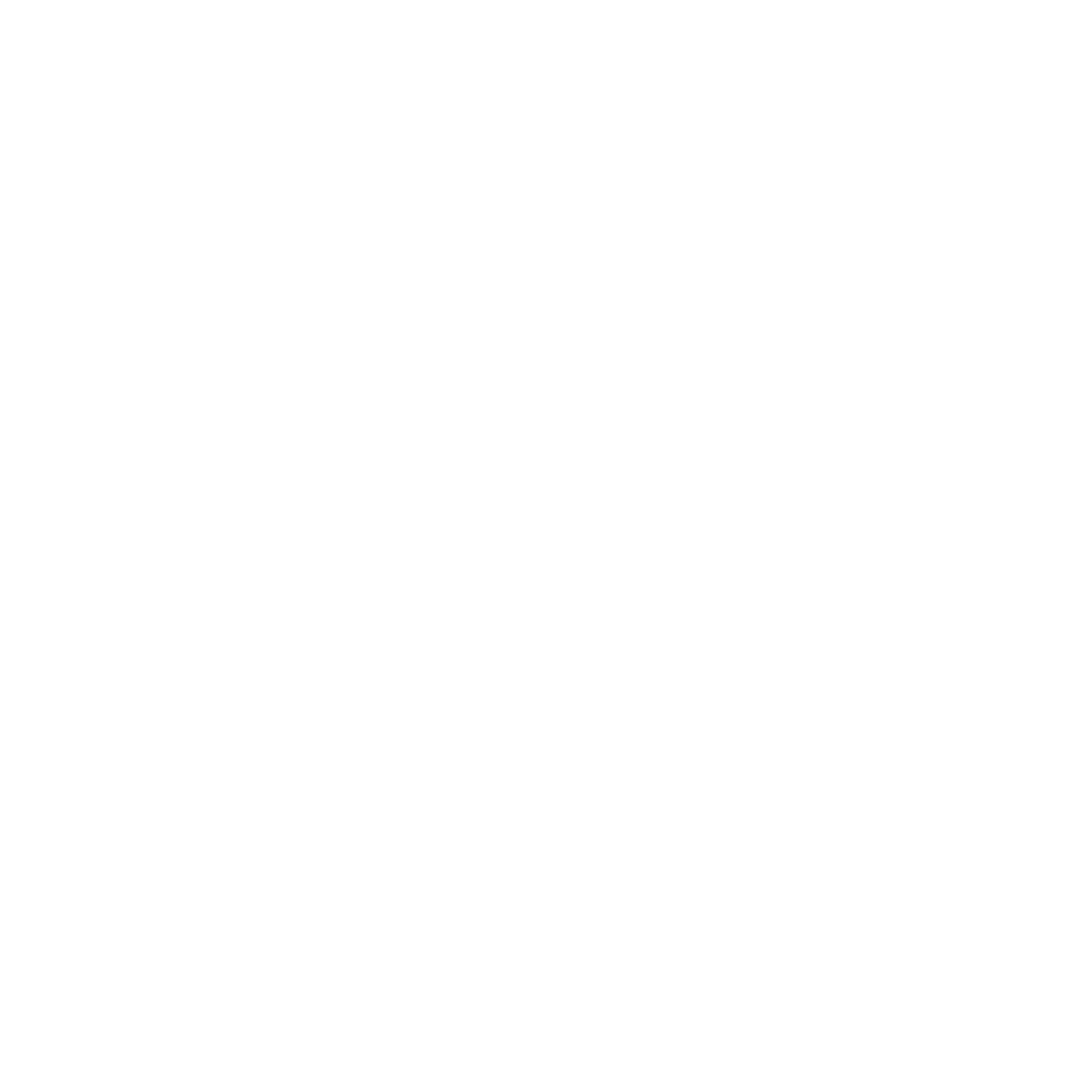
Freezing your eggs (oocyte cryopreservation) can be used to postpone having children while pursuing your educational and professional goals.
Impact of Female Age: Female fertility declines many years before menopause despite continued regular ovulations. The likelihood of a successful pregnancy decreases by approximately 10% to 15% each year after the age of 32 and at an even faster rate after the age of 37. Most women aged 42 and older will require Donor Egg In Vitro Fertilization to have a child.
The successful outcome of the Egg Freezing treatment depends primarily on the patient’s age at the time of egg cryopreservation. It is important to note that the probability of a successful outcome from cryopreserved eggs remains independent of the patient’s age when the eggs are thawed, inseminated, and the resulting embryo(s) transferred into the uterus (the uterus “does not grow old”.
Process of Freezing Eggs:
The Egg Freezing treatment first requires maturing multiple eggs within the ovaries. This process is similar to obtaining multiple eggs in In Vitro Fertilization.
The eggs are then retrieved from the ovaries, cryopreserved, and stored for your future use.
Most patients will be able to continue their everyday lifestyles during their treatment.
No increase in chromosomal abnormalities, birth defects, or developmental deficits has been noted in the children born from cryopreserved eggs.
Egg Cryopreservation consists of:
- Ovarian Stimulation
- Egg Retrieval Procedure
- Cryopreservation of eggs
- Egg storage
Ovarian Stimulation: There are several different forms of ovarian stimulation protocols, each with many modifications. Your treatment is always individualized to maximize the probability of a successful outcome.
An optimal protocol is selected based on your reproductive history and pre-treatment evaluation. Below is an example of an Egg Freezing treatment protocol. Your individualized protocol may take less or more time to complete.
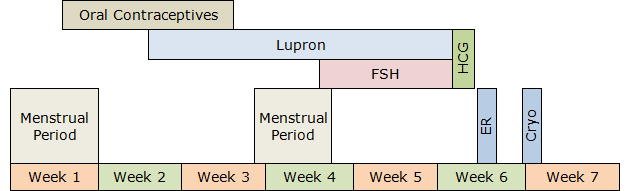
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) or a combination of FSH/luteinizing hormone (LH) hormones will stimulate the production of multiple eggs in the ovaries. They are given subcutaneously once a day with tiny needles for approximately ten days.
During this time, your progress is monitored by estradiol (estrogen, E2) and progesterone blood levels and ultrasound examinations.
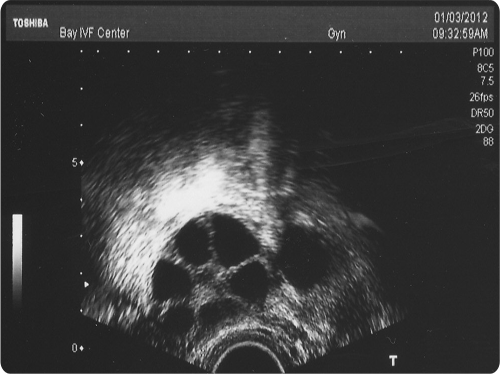
Ovarian stimulation should result in the development of several eggs in each ovary. The ultrasound image below shows a stimulated ovary. Each of the several follicles (dark circles) contains a microscopic egg.
Egg Retrieval Procedure: The procedure only takes a few minutes.
Under ultrasound guidance, the tip of a thin needle is passed through the top of the vagina into the cul-de-sac (space behind the uterus). The ovaries are located near the bottom of the cul-de-sac, allowing the tip of the aspirating needle to enter the ovarian follicles and aspirate the follicular fluid. The fluid is examined under a microscope to identify the eggs.
Cryopreservation of Eggs:
On average, eight to fourteen eggs are aspirated during the egg retrieval procedure. The eggs are identified under the microscope and placed in petri dishes filled with culture medium. The composition of the culture medium resembles the fluid secreted by the Fallopian tubes.
Six hours after the egg retrieval, the eggs are cryopreserved (vitrified). Preparation for the freezing process involves removing water from within the eggs and replacing it with a cryo-protective substance to prevent ice crystal formation during vitrification and subsequent thawing. The eggs are then flashed cooled to −196 °C (−321 °F). Such rapid freezing (vitrification) prevents damaging water crystal formation.
Egg Storage:
After the egg freezing process, the frozen eggs are transferred to a liquid nitrogen storage chamber. Theoretically, there is no limit on the length of storage, but conceiving past the age of 40 may result in a high-risk pregnancy.
When you decide to conceive with your frozen eggs, you will have one or two eggs thawed, fertilized, and transferred inside your uterus. The implantation rate of the thawed fertilized eggs (embryos) is similar to the un-frozen egg embryo implantation rate and, as mentioned above, primarily depends on the patient’s age at the time of egg freezing.
If you are successful, your pregnancy becomes indistinguishable from conception through intercourse, and your obstetrical care should be no different than if you conceived without any treatment.